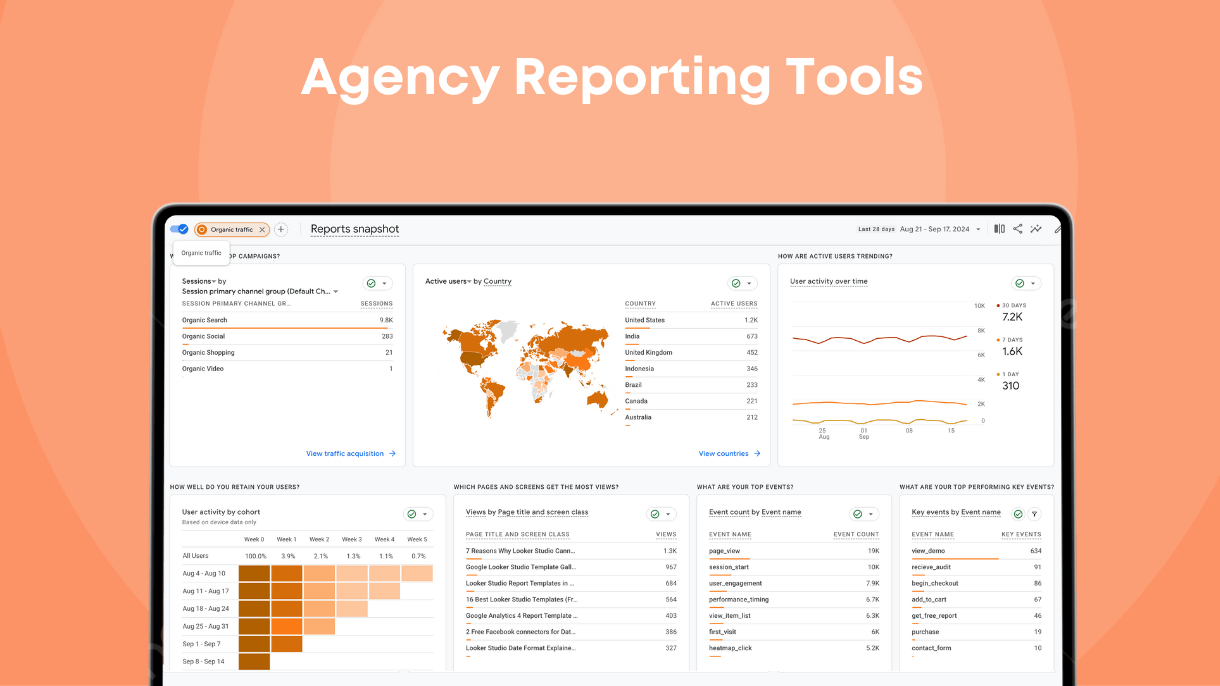
Table of Contents
Google recently announced that Universal Analytics (UA) will eventually be replaced by the newest version of Google Analytics (Google Analytics 4). This post covers the elements of your Google Analytics 4 Checklist and how to run a GA4 audit using Google Data Studio.
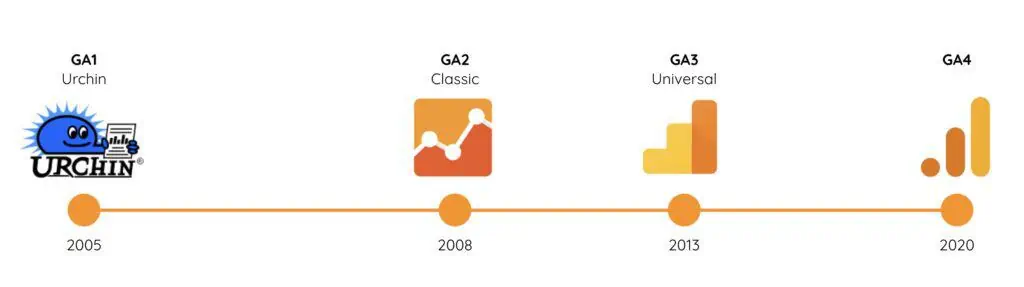
As you probably know Google Analytics is the #1 web analytics platform on the web, as the majority of websites use this platform to measure their online activity and make better business decisions. Google Analytics 4 is the fourth version in the history of GA after acquiring Urchin in November 2005.
Google Analytics Versions:
- 2005 – Urchin
- 2008 – Classic Analytics
- 2013 – Universal Analytics
- 2020 – Google Analytics 4
Measurement Plan
If you are new to Google Analytics, setting up your GA4 property is quite challenging. For this reason, we have gathered all the items that you should have on your list while configuring your GA4 account.
Before starting with any setup process, you should create a measurement plan for your business that will help you to document your actual business objectives and align them with metrics and dimensions you can measure through your analytics platform. Below you will find a quick example of an e-commerce store that wants to increase its revenue through its existing customer base.

Once you complete your measurement plan, you will be able to understand what custom measurement you should have in place so you can track your website goals and KPIs in Google Analytics 4.
Google Analytics 4 Checklist
Here is a checklist that will help you set up GA4 on your site:
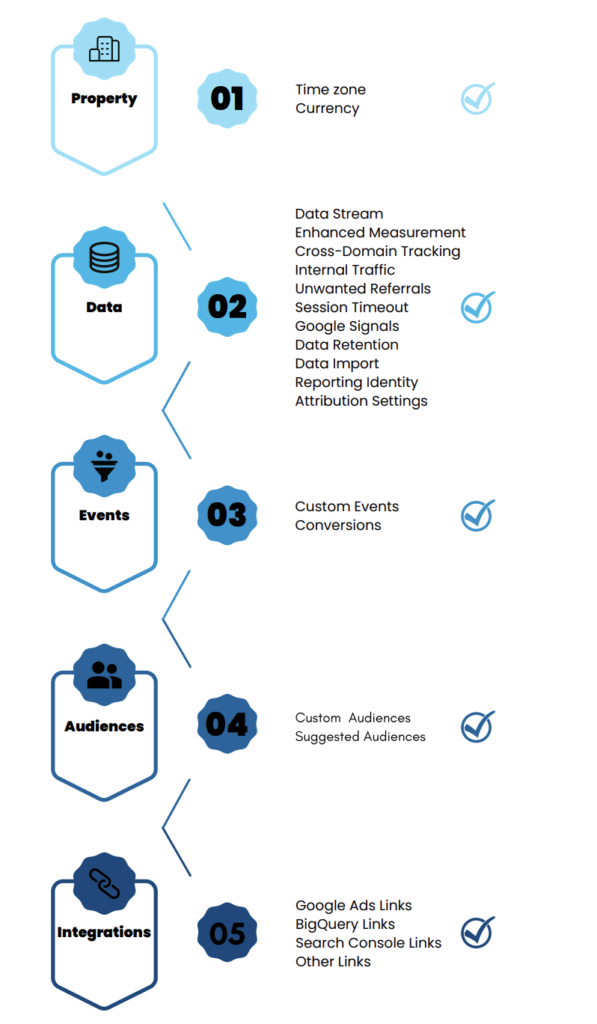
- Property
- Time zone & Currency – Select the right time zone and currency for your business. Have in mind that if you change them later, it will affect your reports. (Admin > Property settings)
- Property Access – Make sure to set the right user roles and proper access to your teammates or external shareholders. You should be the administrator in order to give and edit access to specific users or user groups for GA4 properties. (Admin > Property access management)
- Data
- Data Stream – Choose a platform between website and apps (ios, android) and set up your data stream that will feed your property with the right data. (Admin > Data Streams > Add a Stream)
- Enhanced Measurement – Enable these events in the Google Analytics interface during the initial setup. Fortunately, the enhanced measurement events of GA4 such as scrolls, clicks, site search, and downloads don’t require extra tag implementation – compared to Universal Analytics. (Admin > Data Streams > Select your stream > Enable Enhanced Measurement)
- Cross-Domain Tracking – Include all your domains for cross-domain measurement, so you can easily monitor your users’ engagement across domains. (Admin > Data Streams > Select your stream > More Tagging Settings > Configure Your Domains)
- Internal Traffic – Define your internal IPs in order to block any traffic on your website from your (or colleagues’) activity. (Admin > Data Streams > Select your stream > More Tagging Settings > Define Internal Traffic)
- Unwanted Referrals – Exclude all the referrals such as payment getaways (I.e. Stripe and PayPal) in order to avoid any attribution issues in your reports. (Admin > Data Streams > Select your stream > More Tagging Settings > List Unwanted Referrals)
- Session Timeout (optional) – Adjust the session timeout and the time for engaged sessions to better match your reporting needs. The default time is 30min for a session and 10sec for engaged sessions. (Admin > Data Streams > Select your stream > More Tagging Settings > Adjust Session Timeout)
- Google Signals – Enable Google Signals so you can measure additional features like cross-device audiences and demographics data in your reports. (Admin > Data Settings > Data Collection > Enable Google signals data collection)
- Data Retention – Select the retention period you want to store your users’ data such as cookies, user identifiers, or advertising identifiers. (Admin > Data Settings > Data Retention > Select between 2 or 14 months)
- Data Import – Import external info such as cost, product, user, and offline data to Google Analytics 4. Make sure that the data in your file (CSV) can be joined with Google Analytics. (Admin > Data Import > Create data source)
- Reporting Identity – Choose how your GA identifies your users. The default options are User-ID and device or device only. (Admin > Reporting Identity)
- Attribution Settings – Select the right attribution model for your business that is applied to the standards reports in Google Analytics. (Admin > Attribution Settings)
- Events
- Custom Events – Apart from automatically collected and enhanced measurement (see above 2.1) events, you can create custom events that are tailored to your business, using GA4 interface and/or Google Tag Manager. (Admin > Data Streams > Select your stream > More Tagging Settings > Create Events)
- For instance, if you have an online store, you should create all the required events for enhanced e-commerce such as view_item, add_to_cart, begin_checkout, add_payment_info, and purchase among others.
- Conversions – Mark your main events (KPIs) as conversions. (Configure > Events > Mark as conversion)
- Custom Events – Apart from automatically collected and enhanced measurement (see above 2.1) events, you can create custom events that are tailored to your business, using GA4 interface and/or Google Tag Manager. (Admin > Data Streams > Select your stream > More Tagging Settings > Create Events)
- Audiences
- Custom or Suggested Audiences – Build your custom or prebuilt audience based on your own criteria. (Configure > Audiences > New Audience)
- Integrations
- Google Ads Links – Link your Google Ads account to GA4, so you can measure your paid ads performance inside GA. (Admin > Google Ads Links > Link)
- BigQuery Links – This is a brand new feature for GA4. You can link your BigQuery to GA4 for free. (Admin > BigQuery Links > Link)
- Search Console Links – Link Google Search Console to GA4, so you bring the organic search insights into GA interface. (Admin > Search Console Links > Link)
- Other Links – There are other Google sources that you can connect with GA4 such as Ad Manager, Display & Video 360, Merchant Center, and Search Ads 360. Last but not least, you can sync your Google Optimize with GA, once you have implemented it via Google Tag Manager.
Why You Should Audit Your GA4 Property?
Auditing your GA4 is essential for ensuring that you have properly configured your GA4 property and that it contains accurate and reliable data for your business decisions. Although you may think your data is precise, sometimes many people are relying on inaccurate data due to incorrect setup. This can lead to wasted time and resources on reporting before having checked the configuration part.
An automated GA4 audit like GA4check helps you identify any gaps in the quality and accuracy of your data, enabling you to take the right actions and obtain more precise results. By doing so, you’ll be able to make informed decisions based on reliable information from your GA4 property, improving your business’s overall performance and success.
3 Steps to Audit Your GA4 Property
We have created an automated audit for your Google Analytics 4 account using our knowledge and the capabilities of Looker Studio (previously Data Studio). With just one click and a few seconds, you can easily identify gaps in the quality and accuracy of your data with 25+ actionable checks. Below, we’ll show you three easy steps to run your GA4 audit:
Step 1: Log in to your Gmail account
To audit your GA4 property, you’ll need to log in to the Gmail account that has access to your Google Analytics 4. This will ensure that you have the necessary permissions to access and analyze the data.
Step 2: Open the GA4check tool at GA4check.com
GA4check is an automated tool that can audit your property in just a few seconds for free. Also, it provides actionable insights into over 25 different checks in your property from general configuration and marketing channels to e-commerce and custom events.
Step 3: Select your GA4 property from the data control
Once you’ve logged in to your Gmail account and opened the GA4check tool, you’ll need to select your GA4 property from the data control. The tool will then analyze your data and provide you with a report of any issues it finds in less than 4 seconds.
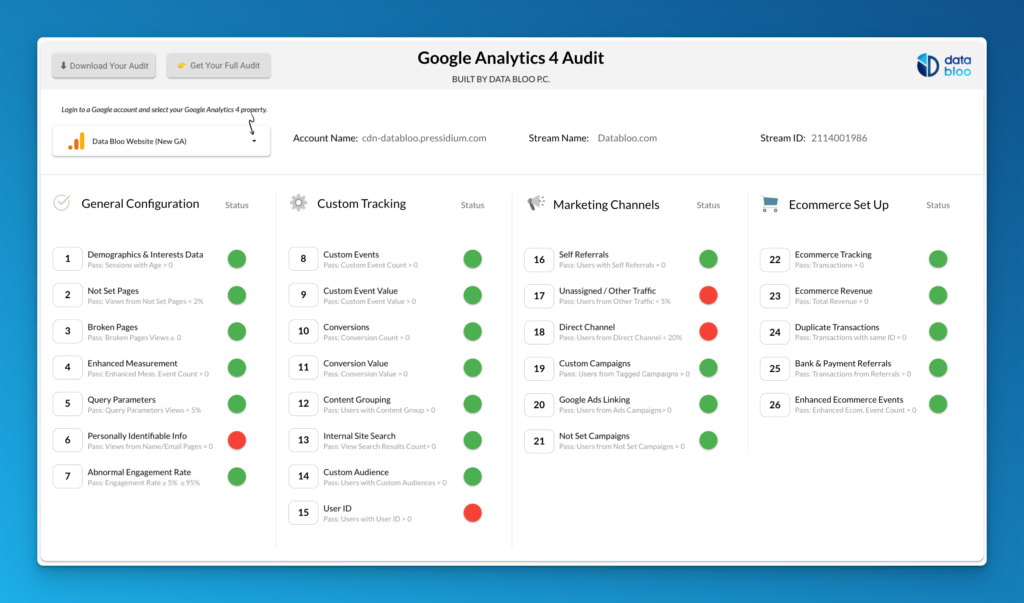
Audit Tool with 25+ Actionable Checks
In this section, we will share more details about all the different checks in the free Google Analytics 4 audit.
General Configuration Checks
1) Demographics & Interests Data
The “Demographics & Interests” check ensures that demographic and interest data is being collected by confirming that sessions with age information are present.
Condition: Sessions with Age > 0
Fail Result: You cannot analyze the website/app behavior per user demographics (age and gender) and interests.
Solution: Activate Google Signals
2) Not Set Pages
The “Not Set Pages” check verifies that there are no pages with missing or incomplete data (i.e., Not Set pages), as this can lead to inaccurate reporting.
Condition: Views from Not Set Pages < 2% (of total)
Fail Result: You cannot measure the pages & screen reports effectively as your website / app receives traffic with no page or screen view level hits included.
Solution: Minimize not set pages
3) Broken Pages
The “Broken Pages” check ensures that there are no broken pages (i.e., pages that return a 404 error) as this can negatively impact user experience and result in incomplete or inaccurate data.
Condition: Views from Broken Pages ≤ 0
Fail Result: You might have user experience issues due to not found (404) pages.
Solution: Fix broken pages
4) Enhanced Measurement
The “Enhanced Measurement” check confirms that Enhanced Measurement is enabled and that at least one event such as file downloads and form interactions has been triggered.
Condition: Enhanced Measurement Event Count > 0
Fail Result: You cannot measure default interactions with your content such as outbound clicks, page scrolls, video engagement, etc.
Solution: Enable enhanced measurement
5) Query Parameters
The “Query Parameters” check verifies that the percentage of views with query parameters (i.e., additional information appended to a page URL) is within an acceptable range, as too many query parameters can negatively impact data accuracy.
Condition: Query Parameters Views < 5% (of total)
Fail Result: You cannot analyze the pages & screens reports effectively due to the query parameters.
Solution: Exclude query parameters
6) Personally Identifiable Information
The “PII” check ensures that no personally identifiable information (PII), such as names or email addresses, is being collected, as this is against Google’s policies.
Condition: Views from Name/Email Pages = 0
Fail Result: Your pages include personally identifiable information that should be removed due to privacy compliance.
Solution: Exclude PII from your URLs
7) Abnormal Engagement Rate
This check ensures that the engagement rate (i.e., the percentage of sessions that resulted in an interaction with the site) is within a normal range, indicating that the site is tracking the user activity properly.
Condition: Engagement Rate ≥ 5% ≤ 95%
Fail Result: You might have measurement issues, as your engagement rate is extremely high/low.
Solution: Fix the engagement rate
Custom Tracking Checks
8) Custom Events
The “Custom Events” check confirms that custom events are being tracked, indicating that site interactions beyond standard events are being captured.
Condition: Custom Event Count > 0
Fail Result: You cannot track specific to your business actions like CTA click, view demo, subscribe to a plan, etc.
Solution: Set up custom events
9) Custom Even Value
The “Custom Event Value” check verifies that custom events are being assigned a value, indicating that they are being used to track valuable site interactions.
Condition: Custom Event Value > 0
Fail Result: You cannot determine the monetary amount associated with the completion of each event.
Solution: Set up event parameters
10) Conversions
The “Conversions” check ensures that conversions are being tracked, which is essential for measuring the most important interactions for your site.
Condition: Conversion Count > 0
Fail Result: You cannot monitor the most important business objectives such as email signup and form submission.
Solution: Set up conversions
11) Conversion Value
The “Conversion Value” check verifies that conversion values are being assigned, indicating that the value of site conversions is being measured.
Condition: Conversion Value > 0
Fail Result: You cannot track the monetary amount assigned to the completion of each conversion.
Solution: Set up event parameters for conversions
12) Content Grouping
The “Content Grouping” check confirms that content grouping is being used, indicating that site content is being categorized for analysis.
Condition: Users with Content Group > 0
Fail Result: You cannot categorize related pages of your website into custom buckets such as Product and Blog pages.
Solution: Set up content grouping
13) Internal Site Search
The “Internal Site Search” check ensures that internal site search is being used, indicating that users are searching for site content.
Condition: View Search Results Count > 0
Fail Result: You cannot identify what users search on your website and if your content is relevant.
Solution: Activate site search event
14) Custom Audience
The “Custom Audience” check confirms the use of custom audiences for targeted marketing based on user behavior, with options for remarketing and prospecting through Google Ads.
Condition: Users with Custom Audiences > 0
Fail Result: You cannot segment your users in ways that are important to your business like remarketing lists.
Solution: Create custom audiences
15) User ID
This “User ID” check verifies that User-ID is being used to measure activity across different sessions and on various devices and platforms.
Condition: Users with User ID > 0
Fail Result: You cannot accurately measure users’ activity across platforms, as different sessions and devices are treated as separate users in Google Analytics.
Solution: Measure activity across platforms with User-ID
Marketing Channels Checks
16) Self Referrals
The “Self Referral” check ensures that self-referrals are not occurring, indicating that site tracking is accurately capturing user behavior.
Condition: Users with Self Referrals = 0
Fail Result: Your website gets traction from self-referrals and the traffic is being attributed incorrectly.
Solution: Configure unwanted referrals
17) Unassigned / Other Traffic
The “Unassigned/Other Traffic” verifies that the percentage of users from unassigned or other traffic sources is within an acceptable range, indicating that site tracking is accurately capturing marketing channels.
Condition: Users from Unassigned/Other Traffic < 5% (of Total)
Fail Result: You might have measurement issues affecting the accuracy of your marketing channels.
Solution: Minimize unassigned traffic
18) Direct Traffic
This “Direct Traffic” check ensures that the percentage of users from the direct channel (i.e., users who typed the site URL directly into their browser) is less than 20% of the total.
Condition: Users from Direct Channel < 20% (of Total)
Fail Result: You might have measurement issues such as incorrectly tagged campaigns.
Solution: Minimize direct channel
19) Custom Campaigns
The “Custom Campaigns” check confirms that custom campaigns are being used, indicating that site traffic is being tracked based on specific marketing campaigns with UTMs.
Condition: Users from Tagged Campaigns > 0
Fail Result: You cannot measure the impact of each marketing campaign effectively.
Solution: Tag your campaigns
20) Google Ads Linking
The “Google Ads Linking” check verifies that Google Ads linking is set up, indicating that site traffic from Google Ads campaigns is being tracked.
Condition: Users from Google Ads Campaigns > 0
Fail Result: You cannot correlate your ads performance with the website/app usage data.
Solution: Link Google Ads and Analytics
21) Not Set Campaigns
The “Not Set Campaigns” check ensures that campaign tracking is set up correctly, and no traffic is being categorized as “not set.”
Condition: Users from Not Set Campaigns = 0
Fail Result: You cannot track the performance of specific campaigns, as the campaign parameters are missing.
Ecommerce Set Up Checks
22) Ecommerce Tracking
The “Ecommerce Tracking” check confirms that ecommerce tracking is set up properly, with at least one transaction recorded.
Condition: Transactions > 0
Fail Result: You cannot measure your ecommerce activity in your app/website.
Solution: Set up ecommerce measurement
23) Ecommerce Revenue
The “Ecommerce Revenue” check verifies that there is a positive total revenue recorded in the ecommerce tracking, indicating that sales value is being monitored through the website.
Condition: Total Revenue > 0
Fail Result: You cannot monitor the total amount that your customers spend on your website/app.
Solution: Set up ecommerce parameters
24) Duplicate Transactions
The “Duplicate Transactions” check ensures that there are no transactions with the same ID, preventing double-counting of sales and other inaccuracies in the data.
Condition: Transactions with same ID = 0
Fail Result: You cannot track the accurate number of transactions as some are recorded multiple times.
Solution: Minimize duplicate transactions
25) Bank & Payment Referrals
The “Bank & Payment Referrals” check detects potential tracking issues where sales are attributed to bank and payment referrals (i.e. PayPal, Stripe) instead of the actual traffic source.
Condition: Transactions from Bank or Payment Referrals > 0
Fail Result: You have tracking issues, as Google Analytics attributes sales to bank & payment referrals.
Solution: Configure unwanted referrals
26) Enhanced Ecommerce Events
The “Enhanced Ecommerce Events” check confirms that Enhanced Ecommerce tracking is set up , with at least one Enhanced Ecommerce event (ie. view item, add to cart) recorded in the specified time period.
Condition: Enhanced Ecommerce Event Count > 0
Fail Result: You cannot analyze the shopping behavior of your customers during the checkout process.
Solution: Set up ecommerce events
Summary
In conclusion, to set up your GA4 property following our comprehensive checklist will help you smoothly migrate from UA to GA4. Apart from that, auditing your GA4 is a quick and easy process that can provide you with valuable insights into the quality and accuracy of your data. By following the three simple steps outlined in this article, you can identify any gaps in your data and fix any issues where necessary, ensuring that you have reliable information to inform your business decisions. So, don’t wait – audit your GA4 property today and take your business to the next level!